Archive for May, 2010
Horoscopes in Arabic Posted by aziza on May 17, 2010
The horoscopes (الابراج) play an important role in some people’s lives – but not me! I have never believed in horoscopes or even cared to read them in the newspaper. This may have some personal or religious reasons. Some people, on the other hand, are obsessed by horoscopes to the extent that they depend on…
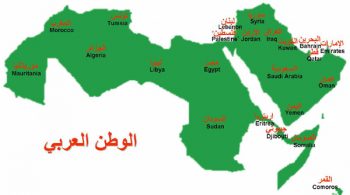
Countries of the Arab World Posted by Transparent Language on May 16, 2010
The names of countries considered to be part of the Arab World including grammatical gender.
The Other Lebanon Posted by Transparent Language on May 15, 2010
Photos of Lebanon by Pascal Beaudenon.
Latifa Al-Zayyat Posted by aziza on May 14, 2010
Latifa Al-Zayyat (لطيفة الزيات) is a distinguished novelist (روائية), literary critic (ناقدة أدبية), an academic (أستاذة جامعية) and an intellectual (مفكرة). She was born in Damietta, on August 8, 1923. She received her education at Egyptian schools and later obtained her PhD in English literature from Cairo University in 1957. She is also a political…
Fronted Predicate in Arabic Posted by aziza on May 11, 2010
In Arabic, nominal sentences typically begin with a subject (مبتدأ), which can be a noun or a pronoun, e.g. الولد طويل. ‘The boy is tall.’ هي طالبة. ‘She is a student.’ A noun that occurs as a subject is often definite, e.g. a proper noun like (محمد) or (نادية), a noun that begins with ال…
Masculine and Feminine Nouns in Arabic Posted by aziza on May 8, 2010
The distinction of gender into masculine (مذكر) and feminine (مؤنث) is an important feature of Arabic, unlike English where grammatically the great majority of words do not make this distinction clear, e.g. in English ‘student’ does not imply the gender of the person it refers to, while in Arabic (طالب) is masculine while (طالبة) is…
Arabic Musical Instruments: The Derbake Posted by Transparent Language on May 4, 2010
The Arabic drum, or the derbake, that I recently purchased in order to learn the instrument.